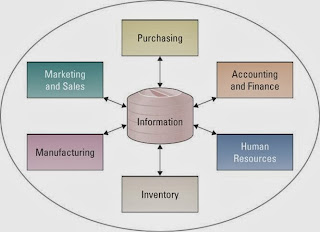
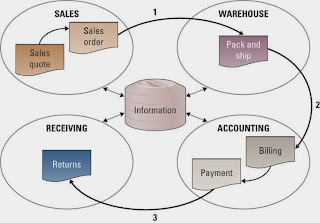
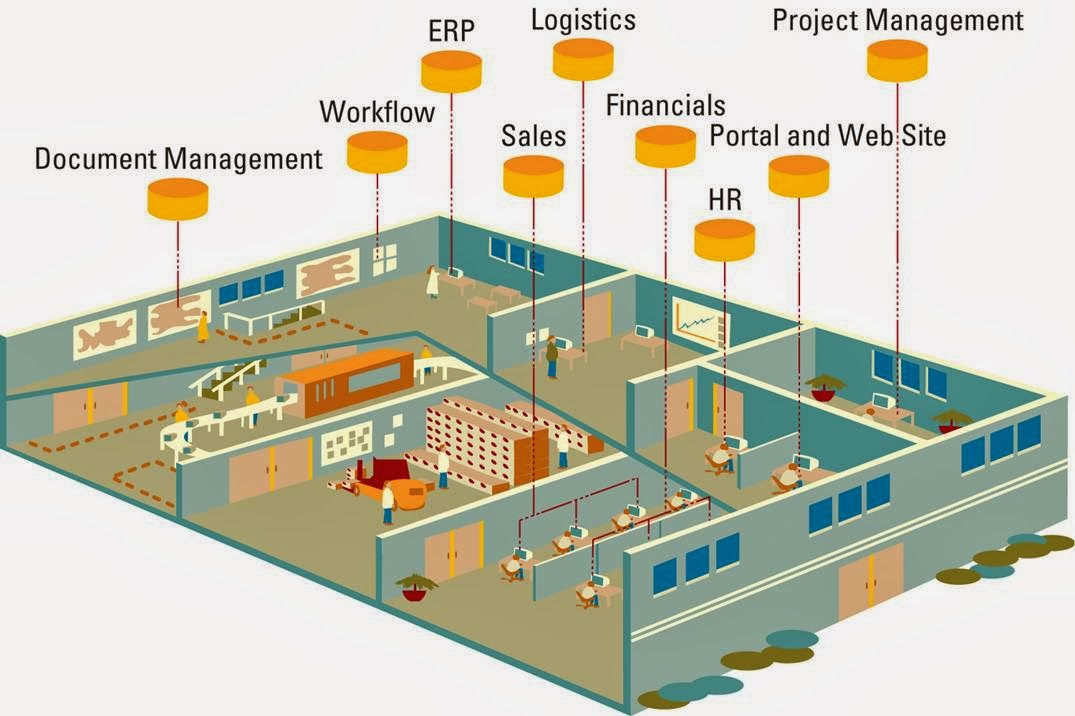
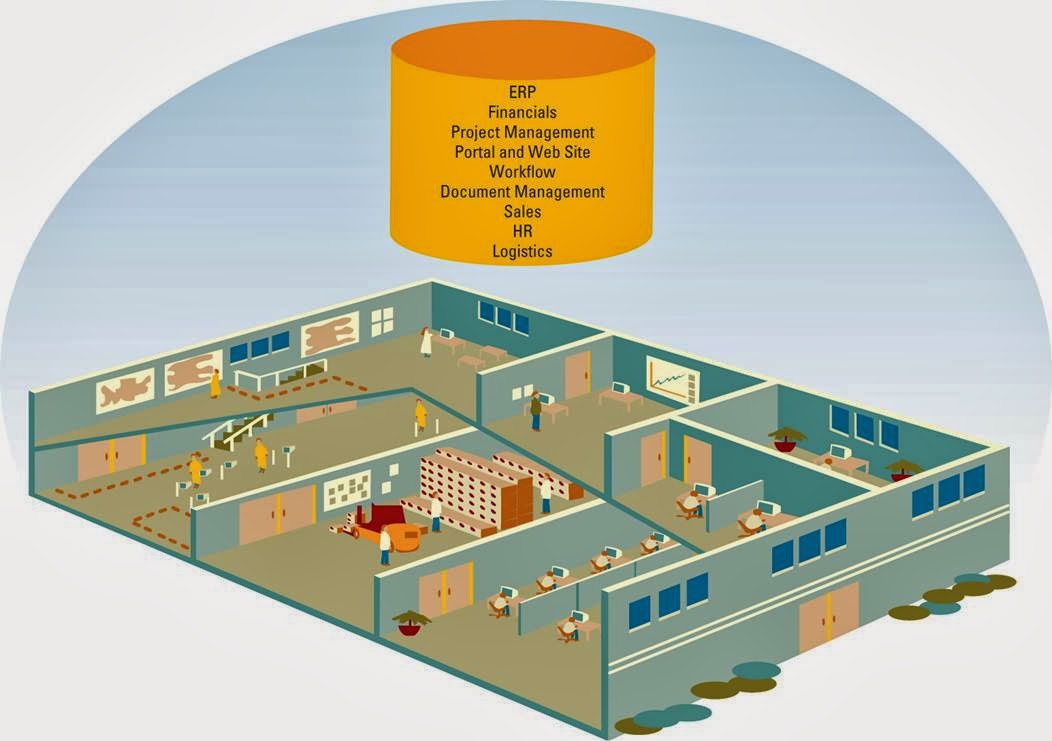
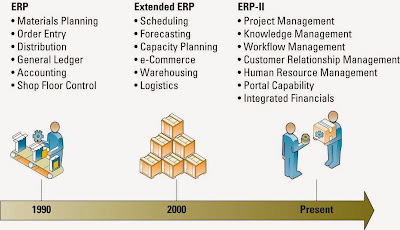
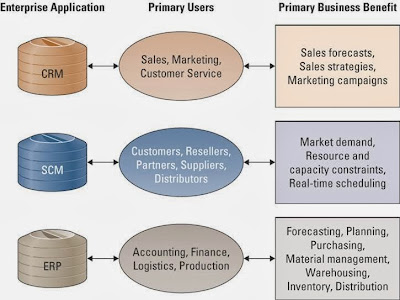
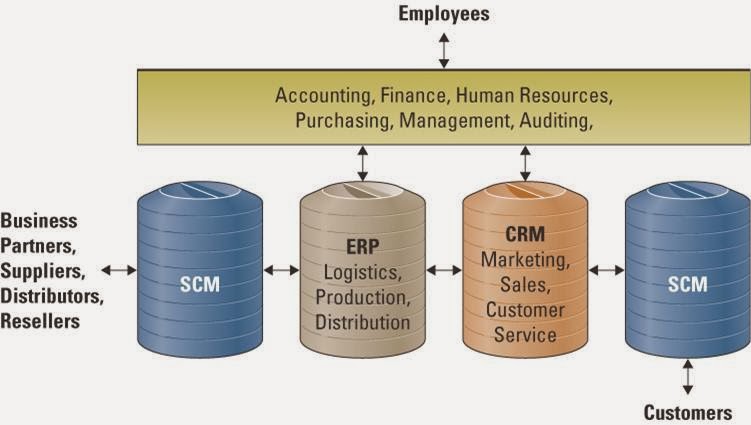
Insourcing ( in - house development ) - is a common approach
using the professional expertise within an organization to develop and
maintain the organization's information technology systems.
Outsourcing - is an arrangement by which one organization
provides a service or services for another organization that chooses not
to perform them in-house.
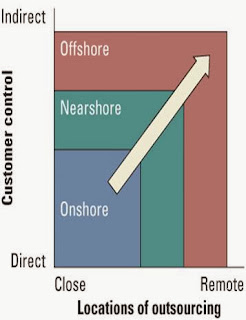
Three different forms of outsourcing options a project must consider
- Onshore outsourcing - engaging another company within the same country for services.
- Nearshore outsourcing - contracting an outsourcing arrangement with a company in a nearby country. Often this country will share a border with the native country.
- Offshore outsourcing - using organizations from developing countries to write code and develop systems. In offshore outsourcing the country is geographically far away.
Influential drivers affecting the growth of outsourcing market
- core compentencies
- financial savings
- rapid growth
- industry changes
- the internet
- globalization
- increased quality and efficiency
- reduced operating expenses
- outsourcing non-core processes
- reduced exposure to risk
- economies of scle, expertise, and best practices
- access to advanced technologies
- increased flexibility
- avoid costly outlay of capital funds
- reduces headcount and associated overhead expense
- reduced time to market for products or services
Outsourcing Challenges
- contract length
- difficulties in getting out of a contract
- problems in foreseeing future needs
- problems in reforming an internal IT department after the contract is finished
- competitive edge
- confidentiality
- scope definition